COMPARISON: AUTOMATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR (AED) VS. IMPLANTABLE CARDIOVERTER DEFIBRILLATOR (ICD) | WELLBEING
The Automated External Defibrillator (AED) and the Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) are two distinct devices regarding their operation and application. Below are the key differences between these two types of devices:
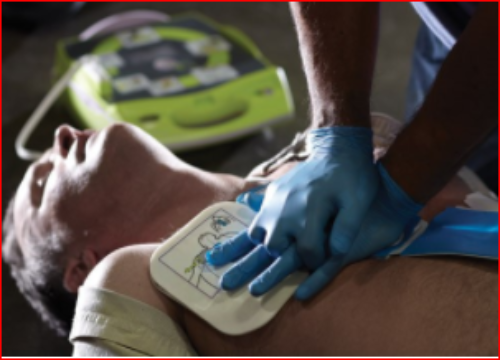
1. Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
-
External Use: The AED is used externally (outside the body) during emergency situations involving Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) or abnormal heart rhythms. It is designed for immediate rescue and can be operated by lay rescuers (non-medical personnel).
-
Automated Analysis and Shock Delivery: The AED automatically analyzes the heart rhythm to determine if an electrical shock is necessary for defibrillation. If required, the device provides voice/visual guidance on placing electrode pads on the victim's chest and delivers the shock automatically to restore a normal rhythm.
-
Widespread Public Availability: AEDs are commonly found in medical facilities, public spaces, fitness centers, and corporate offices. They are installed in accessible locations to ensure that bystanders can perform life-saving interventions during an emergency.
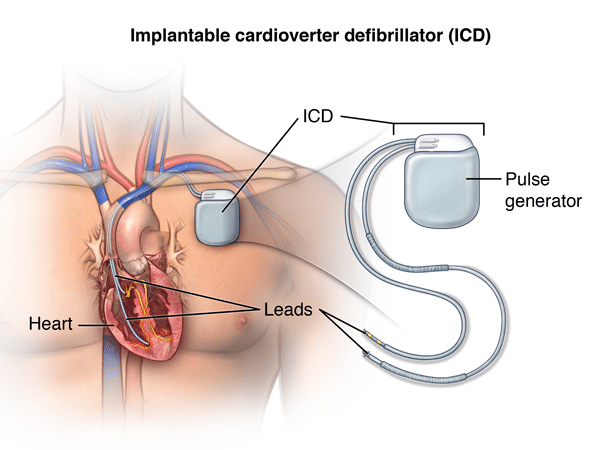
2. Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
-
Implanted into the Body: The ICD is a medical device implanted inside the patient's body via a surgical procedure. It is typically placed under the skin near the collarbone and connected to the heart via electrode leads to monitor and regulate heart rhythm.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Automatic Intervention: The ICD operates 24/7, continuously monitoring the patient's heart rate to detect abnormalities. If a dangerous arrhythmia occurs, the device automatically delivers a low or high-energy internal shock to defibrillate and restore a normal rhythm immediately.
-
For High-Risk Patients: ICDs are typically prescribed for individuals at high risk of life-threatening cardiac conditions, such as severe ventricular arrhythmias, history of cardiac arrest, or coronary artery disease. The device serves as a long-term safeguard to prevent sudden cardiac death.
In Summary: The AED is an external device used for emergency rescue by bystanders when cardiac arrest occurs. Conversely, the ICD is an internal device surgically implanted to continuously monitor and regulate heart rhythm for patients with a history of high-risk heart disease.
Comments:
There are no comment for this news.
 Tiếng anh
Tiếng anh  Vietnam
Vietnam 




.png)
.png)

